Ofer Miller, Ph.D.
Computer Vision . Image processing . Graph Theory Models . Video Analysis
Ph.D. in Computer science | Researcher in Computational Imaging & Signal analysis
Main Menu
*Internal Links
*External Links
Education,
(its still the most Important.....)
Ph.D. Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University, Israel .
Research interests: Computer Vision, Image Processing and Signal Understanding.
Concentrations: Graph theory models in adaptive linear segmentation for video processing.
Dissertation: Advanced Spatial and Temporal Segmentation models and Their Applications.M.Sc. Computer Science , cum-laude, Tel-Aviv University, Israel.
Research interests: Image Processing (models of Illumination in still images)
Thesis: Illumination independent change detection algorithm in a pair of gray images based on connectivity analysis along gray levelsB.A. Computer Science, Tel-Aviv Academic College, Israel .
Concentrations: Graph theory models.
***It important to mention here my deepest gratitude to my doctoral supervisor , Professor Amir Averbuch . I am profoundly thankful to Amir, whose enthusiasm, patience, wisdom, and unwavering dedication to his students proved invaluable—particularly during moments when the task at hand appeared daunting. The academic freedom Amir granted for the exploration of new ideas and approaches, while simultaneously guiding me in the right direction, rendered the four years of research under his mentorship both engaging and intellectually stimulating.
HONORS AND AWARDS
• "Celia and Marcos Maus Annual Prize“ in Informatik für herausragende Leistungen in der Promotionsforschung, Mai 2002• Exzellenzstipendium für Doktoranden vom Rat für Hochschulbildung im Bereich Hochtechnologie, Dezember 2000• Auszeichnung der Universität Tel Aviv für hervorragende Leistungen im Masterstudium der Wissenschaften, Juni 1999• Stipendium der Universität Tel Aviv für Masterstudierende der Wissenschaften, Oktober 1998


Publications (Contribute to Science)
List of Patents
| Title | Author | Year | Patent#: |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. "Determine Viewer's exposer to Visual Messages" | Ofer Miller | 2016 | 20170169464 |
| 2. "Method for logging a user in to a mobile device" | Ofer Miller | 2015 | 20150049922 |
| 3. Method for rating areas in video frames | Ofer Miller... | 2013 | 8457402 |
| 4. Method and Device for Processing Video Frames | Ofer Miller... | 2012 | 20120017238 |
| 5. System and Method for Enriching Video Data | Ofer Miller... | 2011 | 20110217022 |
| 6. Method for illumination independent change detection in a pair of registered gray images | Ofer Miller... | 2006 | 7088863 |
| 7. Automatic object extraction | Ofer Miller... | 2006 | 7085401 |

Research contribution during studies at TLV University
Illumination independent Object based Change Detection Article
Video Graph based Segmentation of Moving Objects while spatial and temporal information are available.
Still Image Segmentation Based on Adaptive Local Thresholds
Tracking of Moving Objects Based on Matching between Graph Edges
Contribution to Artimedia Initiative
Foundations of Computer Vision
Lets be clear : Artificial intelligence is built upon the entirety of humanity’s accumulated knowledge; it simply leverages this knowledge more efficiently and at by far greater speed.
Let me clarify some of the basic challenges :
Human vision naturally interprets and understands the surrounding world as a three-dimensional (3D) environment. In contrast, most of the common visual sensors such as cameras still capture only two-dimensional (2D) projections of this world. During the projection from 3D to 2D, a significant amount of information—particularly depth information is lost. While humans are able to effortlessly interpret the dynamic structure of 2D image sequences, achieving comparable understanding computationally is challenging, especially when relying on a single visual sensor. Although using multiple sensors can facilitate 3D reconstruction, many multimedia applications rely on a single-sensor setup, making the absence of explicit 3D information one of the fundamental challenges in computer vision. Consequently, the effective use of spatial and temporal cues becomes essential for understanding the dynamic structure of scenes captured with a single camera.Complexity note:
In much of my bellow public research, I rely on graph-based data structures and their associated algorithms including : breadth-first-search (BFS), depth-first-search (DFS), graph contraction, minimum spanning tree (MST), finding k shortest path between two vertices, to obtain efficient implementations. Thus, provides a set of related constructive algorithms for high-level processing that has linear, almost-linear and polynomial time complexity. Linear or almost linear time-complexity algorithms are proportional to the image size n. Thus , Its enables getting a polynomial time complexity for some algorithms when the complexity is proportional to number of arcs E in the image segmentation boundaries. Then the complexity becomes O(E x E) rather than O(N x N) and E<<N.
Segmentation
Is it possible to segment "correctly" on still Images ? (while no motion info available)
Still Image Segmentation Based on Adaptive Local Thresholds!!!!
An algorithm that integrates edges and region-based techniques while local information is considered. The local consideration enables to derive local thresholds adaptively such that any threshold is associated with a specific region represented by graph. The number of thresholds is automatically determined during the process, which is also automatically terminated
Here is the official publication Link of the above article.
What's happens when we have both saptio and temporal information
Graph based Segmentation of Moving Objects Based on Connectivity Analysis of Spatio-temporal information
Lets dive into a Segmentation algorithm for separating moving objects from the background in video sequences without any prior information of their nature !. I formulate the problem as a connectivity analysis of region adjacency graph (RAG) based on temporal information. By performing a watershed based algorithm I managed to segment the frame into a semantic homogeneous region. The boundary pixels in each region are compared with a series of consecutive frames in order to generate temporal information. The edges of the RAG will represents the temporal information. Each node represents a different homogeneous region. Analysis of the RAG's connectivity is achieved by performing a modification of the breadth-first-search (BFS) algorithm. After a sufficient number of comparisons each of the object's components is merged into a single segment which represents the moving object in the frame. The accuracy of the algorithm is proportional to the number of allowed comparisons.
Here is the official publication Link of the above article.
Change Detection
Identify changes between two gray images taken in extreme! different illumination, is it possible ?
Illumination independent change detection technique between two gray images, it possible !
The goal of such algorithm is to extract the objects that appear only in one of two registered images. A typical application is surveillance, where a scene is sampled at different time gap. Assumption of significant illumination difference between the two images is considered. For example, one image may be captured during daylight while the other image may be captured at night with infrared device. Now the secret for the solution here is by analyzing the connectivity along gray-levels, all the blobs that are candidates to be classified as ‘change’ are extracted from both images. Then, the candidate blobs from both images are analyzed. A Blob from one image that has no matched blob in the other image is considered as a ‘change’. The algorithm is reliable, fast, accurate, and robust even under significant changes in illumination. The worst-case time complexity of the algorithm is almost linear in the image size. Therefore, it is suitable for real-time applications.
Here is the publication Link of the above article.
The algorithms was considered to be the Most Cited paper !

Smart Tracking
Track after occluded objects in linear complexity ?
Yes !! , but for linear complexity, a graph based theory algorithm is required
The above Algorithm suggests a novel algorithm for tracking moving objects in video sequences. The proposed algorithm is contour-based. The region adjacency graph (RAG) that is obtained from the segmentation results of the input frame, is used to segment the object's contour into subcurves. Then, each connection between two subcurves is called an 'important' junction. The motion of the junctions is estimated in a search that is represented by the RAG edges in the consecutive frame. Each pair of matched junctions may be connected by several edge paths that are candidates to represent the tracked contour. The candidate paths are obtained by an algorithm that finds the k shortest paths between two nodes. It operates on an RAG that is transformed into a weighted and directed graph. Finally, a construction of the tracked contour is achieved by a match process between the object edges and the set of candidate paths.
Here is the publication Link of the above article.
AI & Computer Vision
What is the AI algorithm ? how its evolved ?
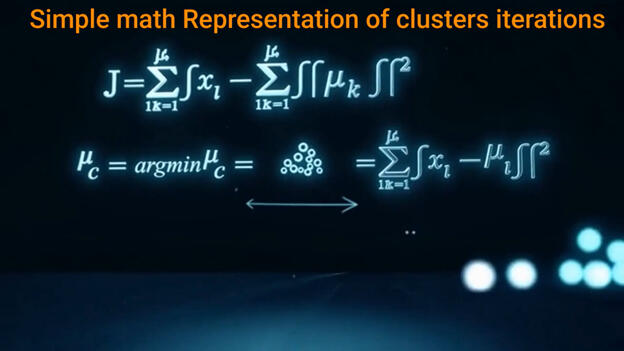
Lets start with understanding of what is The K-means algorithm: so its an unsupervised machine learning algorithm used to group data points into k clusters based on their similarity, with each data point assigned to the cluster with the nearest centroid (cluster center). It works by iteratively assigning data points to clusters and then updating the centroids to the mean of the assigned points, repeating the process until no data points change cluster membership. K-means is useful for applications like customer segmentation and image analysis but requires the number of clusters (k) to be specified beforehand and is best at finding spherical clusters.
Artificial intelligence systems operate by learning statistical patterns from data and using those patterns to make predictions or decisions. At their core, modern AI models, especially deep neural networks, optimize a large set of parameters through iterative training, where the algorithm compares its predicted output to the correct output, computes an error, and adjusts internal weights using gradient-based optimization methods such as backpropagation. Through repeated exposure to vast amounts of labeled or unlabeled data, the model gradually minimizes this error and forms a high-dimensional representation of the underlying structure of the problem. Once trained, the AI system applies these learned representations to new inputs, enabling tasks such as classification, pattern recognition, reasoning, and generative output.
Now , lets jump all the way trying to describe the link between the basic k-means concept and the AI algorithms :
So the k-means algorithm, while not a learning model in the sense of deep neural networks, is a foundational unsupervised machine-learning method that contributes to the broader architecture of artificial intelligence. Through an iterative process of assigning data points to the nearest centroid and recomputing those centroids, k-means minimizes intra-cluster variance and produces a compact representation of complex datasets. In the context of AI, k-means plays the main role as a preprocessing or feature-extraction, and representation-learning tool. It is used to reduce dimensionality before training neural networks, to initialize parameters in deep models. More broadly, k-means embodies the principle that AI systems often learn by organizing and compressing information in structured ways, enabling models to generalize from raw data to meaningful abstractions.
so , what we have here ??, conceptually, AI particularly is a deep learning, can be viewed as a vast generalization of the principles embodied in k-means clustering. while k-means partitions data in a relatively simple Euclidean space by assigning each point to the nearest centroid, deep neural networks expand this notion into extremely high-dimensional, learned feature spaces. In these spaces, the model implicitly performs a form of dynamic clustering: representations of similar inputs are projected into nearby regions, while dissimilar inputs are pushed apart. Thus, AI systems can be interpreted as applying k-means-like separation but across hundreds or thousands of learned dimensions, with the boundaries not fixed by geometry alone but continually adjusted through gradient-based optimization. In this sense, the core intuition of k-means grouping similar patterns is preserved, while the expressive capacity is vastly expanded to support abstraction, generalization, and complex decision-making. so , just for those who like visual , here its how its look like :
Graph Model Representation
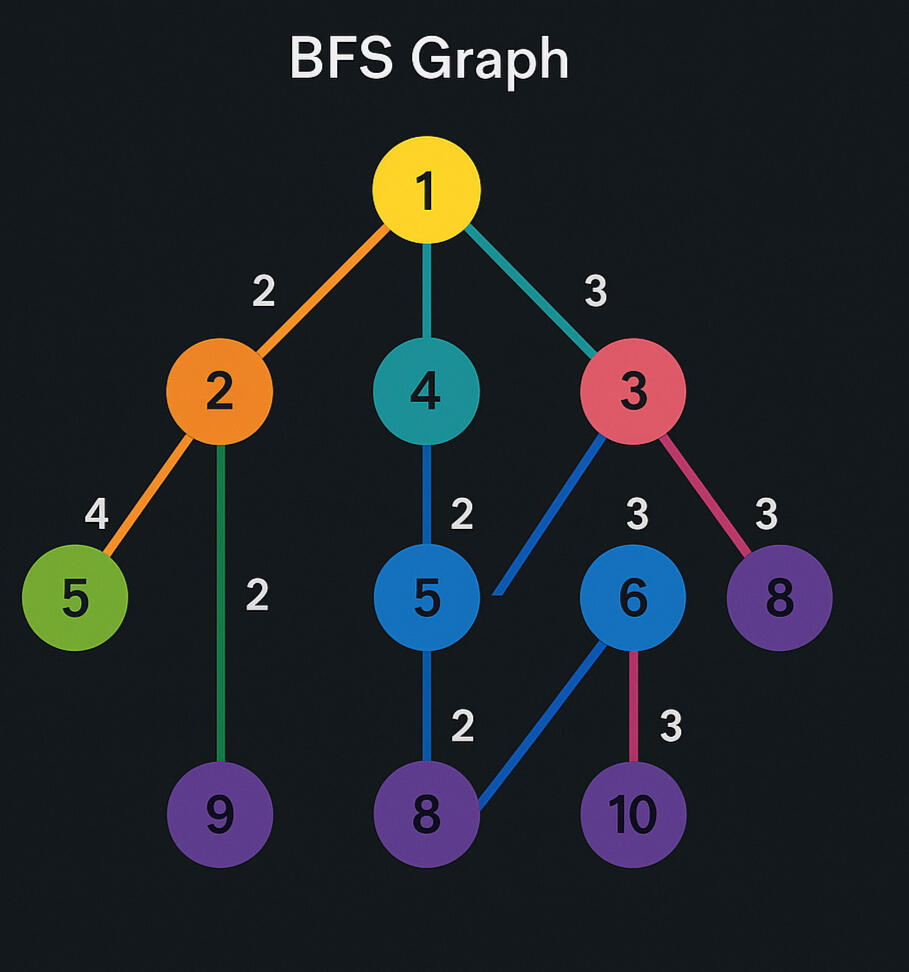
Breadth-First Search (BFS) is a fundamental graph-traversal algorithm that explores the vertices of a graph level by level. Given a graph 𝐺 = (𝑉,𝐸) G=(V,E), BFS begins from a seed vertex 𝑣0 ∈ 𝑉 and visits all vertices at distance 1, then all vertices at distance 2, and so forth. It uses a queue to ensure first-in/first-out (FIFO) processing of nodes, guaranteeing that the shortest path (in terms of edge count) from 𝑣0 v 0 to any reachable vertex is discovered.
First Stage
now , the images can be modeled as graphs in the following way :Each pixel is a vertex (Node):
𝑣 𝑖 , 𝑗 ∈ 𝑉Edges connect neighboring pixels according to a connectivity rule (4- or 8-connected in 2-D), so
𝐸 = { ( 𝑣 𝑖 , 𝑗 , 𝑣 𝑚 , 𝑛 ) : ∥ ( 𝑖 , 𝑗 ) − ( 𝑚 , 𝑛) ∥ 1 = 1 or ∥ ( 𝑖 , 𝑗) − (𝑚,𝑛) ∥ ∞ =1 } E={(v i,j ,v m,n ):∥(i,j)−(m,n) ∥ 1
=1 or ∥(i,j)−(m,n)∥ ∞ =1}
Second Stage
Given a seed pixel, BFS expands to all neighboring pixels that satisfy a similarity condition (e.g., intensity difference < threshold). This forms a segmented region.
Third Stage (representation)
Mathematical Representation
1. Graph ModelA 2-D image
𝐼 of size 𝑀 × 𝑁
M×N is represented as a grid graph:
𝐺 = ( 𝑉 , 𝐸 ) , 𝑉 = {(𝑖 , 𝑗 ) ∣ 1 ≤ 𝑖 ≤ 𝑀 , 1 ≤ 𝑗 ≤ 𝑁 }.
G=(V,E),V={(i,j) ∣ 1≤i≤M, 1≤j≤N}.Edges:
𝐸 = { ( ( 𝑖 , 𝑗 ) , ( 𝑚 , 𝑛 ) ) ∣ ( 𝑚 , 𝑛 ) ∈ 𝑁 ( 𝑖 , 𝑗 ) } , E={((i,j),(m,n)) ∣ (m,n)∈N(i,j)},
where
𝑁 ( 𝑖 , 𝑗 )
N(i,j) is the 4- or 8-connected neighborhood.
In Short : BFS is a level-ordered graph-traversal algorithm that, in image processing, is used for connected-component labeling, region growing, flood-fill, and geodesic distance computation. Mathematically, the image is a grid graph 𝐺 = ( 𝑉 , 𝐸 ) where each pixel is a vertex connected to its neighbors. BFS computes the shortest discrete distance from a seed and expands regions based on similarity predicates, making it a core tool in graph-theoretic image segmentation.